Rising Sea-levels a Significant Urban Economic Hazard
The image of sea level rising because of global warming, tends to bring into mind the scenario where beaches are getting eroded and countries such as Maldives getting submerged. But in reality, the effect is mostly significant in the major cities and not in coastal towns and island nations.
These are several important points shown by McKinsey in the 2011 economic projection report, Urban world: Mapping the economic power of cities:
Currently, 600 urban cities are responsible for over 60% of world’s GDP. By the year 2025, there will be an addition of another new 136 cities within that 600, each and every one of them located in the developing world and a staggering 100 based in China. At present, 23 megacities with a population exceeding over 10 million or more, will ultimately boost world’s growth by 10% by 2025, below their 14% of the global GDP.
Although several of the cities are located at the sea-level, others are not. There is a considerable geographical variation seen amongst these cities. Below are the top 10 of the 25 cities as per McKinsey report and their shifting status projected by numerous metrics.
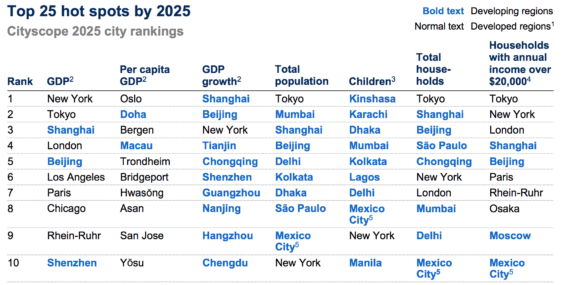
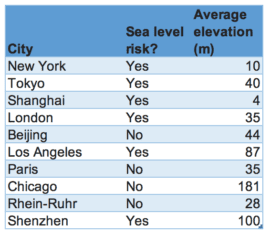
Only six of the ten largest GDP cities are facing possible exposure to rising sea levels. As per the current projections, by the year 2100 the sea level would have risen by a meter. IPCC 5 has stated a median of 60 cm or 2 feet, but rejected several papers which projected a greater increase due to the inadequacy to provide an explanation. There has been increased research since then.
The other important factor is that sea level increases shows a considerable variation. It is greater at the equator and at the poles of the earth due to the centripetal force present along with thermal expansion. Tokyo is estimated to face an increase of the sea level in the range of 45% more than the average predicted. It will approximately be 1.5 meters or 5 feet.
The rising sea level is only one of the issues. Majority of these coastal cities are exposed to increased natural calamities in the form of cyclones, in the Asian region typhons have hit land at in increased severity and frequency as compared to the past four decades. Hurricane Sandy which affected New York to Harvey which affected Houston, increased damage is seen due to the increased strength, size and moisture content of these storms. Storms are generally associated with increased surges ranging several meters in height and rains which results in inland flooding with the storm surges.
What effect would be seen in the fastest growing cities by the year 2025?
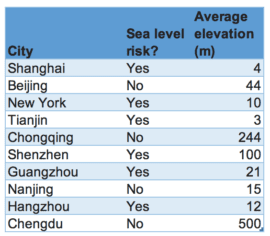
According to McKinsey, a couple of the cities have been pushed downwards from the top ten, there are still six cities facing the possible effect of rise of sea level. The average elevation of the cities has risen from 56 to 95 meters, but this measurement is not useful. The most important fact is that these cities are located inland and not in close proximity to the sea.
The new cities show both strengths and weakness in certain regards. A main strength is that majority of these cities are based in China which possesses a command-and-control economy which realizes the effect of increasing sea levels and are taking appropriate steps to counteract it. Their growth and cities being located in strategic economic zones would assist them to be more resilient in the face of such adversity. A major downside is that the legacy Asian cities are less resilient in comparison to New York and Tokyo owing the minimal resilience investments done over the past couple of decades.
Would there be an effect on economic growth with the increasing sea levels? Absolutely and negatively. Expensive infrastructure would be abandoned or would necessitate significant and costly protection measures. The money utilized although being an economic driver could have been used to achieve far more useful economic growth.
Will there be an equivalent effect on the seaside cities? No, Miami, which is not featuring on the top 25 cities would see significant damage owing to numerous reasons such as increasing sea level, costal subsidence and porous limestone. Dhaka which is not on the list could possible face 27 million people affected by the rising sea level by the year 2050. It was affected in 2017 by the monsoon flooding which was mostly limited to the northern part of the city.
Will the earth’s economy survive? Yes, it would. Would be realize a decreased economic growth? Yes.
One projection puts the economic burden at 14 trillion USD by 2100. Another projection has placed a loss of a trillion USD in U.S. These are considerable amounts of money. The worlds GDP is currently at 78 trillion USD at the present.
This is the main reason why governments considering the economy consequences have united with their people have taken steps to minimize the effect of global warming. It is also the main reason why it is disheartening to see the regression of USA, which is affecting the citizens of USA but also the entire world.
